Biopsy (All Types)
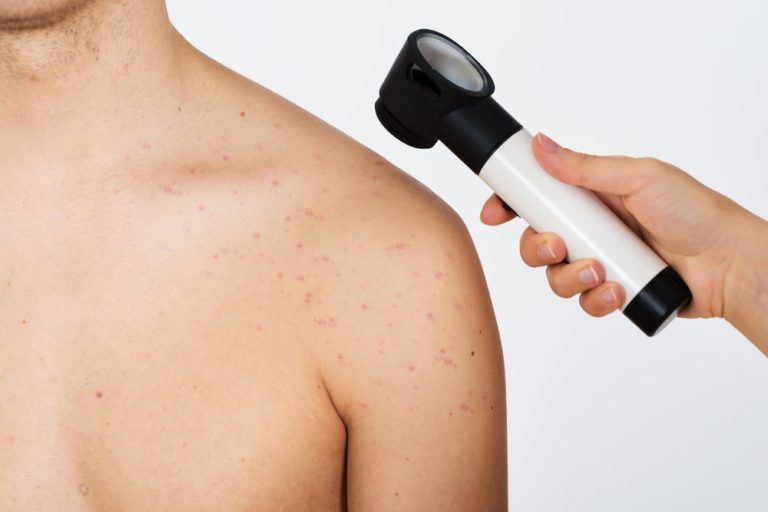
Your skin is the largest and most visible organ in your body, working hard to protect you from your environment. Though it may not be treated with as much attention as other major organs, such as the heart and liver, the skin plays an essential role in overall health. It is important to be vigilant in caring for the skin, carefully inspecting it for signs of potential health problems. When a lesion or suspicious growth threatens the body, a skin biopsy may be necessary to diagnose the lesion either as malignant or benign.
Skin biopsies are most commonly requested to evaluate skin discoloration, growths, or even simple moles that have recently changed in shape, texture, size or color. During a biopsy, a doctor will take a small sampling of the suspicious tissues and send them to a lab for microbiological analysis. The results of a skin biopsy help doctors determine the best course of treatment for the patient if necessary.
Did you know…
that there are three different types of skin biopsies? The type of biopsy used usually depends on the size and depth of the lesion. The shaving method is the most common and also least invasive. It involves taking a small shaving of the skin using a sharp instrument, such as a scalpel. Punch, excisional and incisional biopsies are also used though they are slightly more invasive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a skin biopsy?
You may need a skin biopsy if you have blemishes, moles, or imperfections on your skin with characteristics that have changed in appearance or texture over the past few weeks or months. Although many skin growths are benign, the only way to know for sure is via pathological testing. Most skin cancers are highly treatable in their earliest stages, but allowing them to progress without treatment can allow cancer to spread into the lymph nodes or other areas of the body. To find out if you need to have any part of your skin biopsied, contact your a general surgeon to schedule a consultation.
What should I expect during a skin biopsy?
Before your biopsy is taken, your doctor or a nurse will cleanse the area to be biopsied and administer a local anesthetic. This will ensure you feel no pain or discomfort during the procedure, which usually takes just minutes to complete. Following tissue collection, your doctor will apply pressure to stop any bleeding and bandage it to better facilitate healing. Your pathology report may be ready within a few days.
Will I experience a recovery period after getting my skin biopsied?
Many biopsy sites are wounds that will take the time to heal. Your skin may be sutured and treated with a topical antibiotic ointment in the office before you leave. Depending on the extent of the biopsy, you may need to return to your general surgeon’s office for a follow-up or to have the dressing on your wound changed. Once your pathology review information comes back, you will be given the results along with any recommendations for treatment or further testing.


